4/16
Bioengineering
Researchers identify potential nanoparticles for therapeutic mRNA delivery before birth
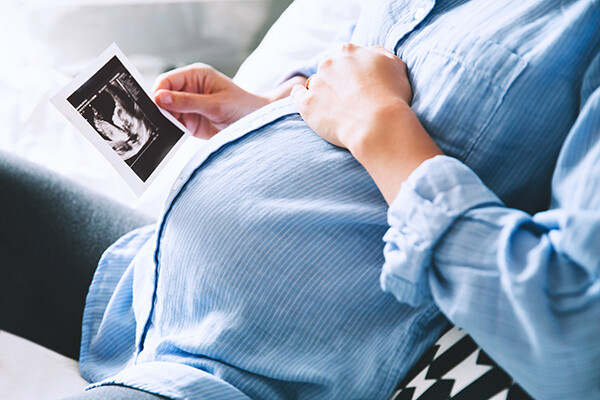
Researchers at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the School of Engineering and Applied Science have identified ionizable lipid nanoparticles that could be used to deliver mRNA as part of fetal therapy.
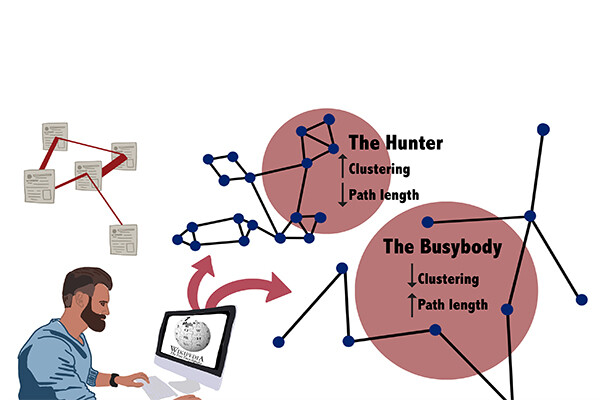
Researchers measure different types of curiosity studying ‘hunters and busybodies’
A multidisciplinary study has found a way to readily quantify the information-seeking associated with curiosity and explore mechanisms underlying information-seeking.
Ruby Washington is poised to make her mark in bioengineering
The senior in Penn Engineering’s Department of Bioengineering weds biomedicine and her pursuit in addressing healthcare disparities in the Black community.
One step closer to an at-home, rapid COVID-19 test
The lab of César de la Fuente is working on a paper-based biosensor that could provide results in minutes. Clinical trials began Jan. 5.
Using lung-on-a-chip technology to find treatments for chlorine gas exposure
The new lung-on-a-chip platforms will help better understand how chlorine damages lung tissues and to discover specific biomarkers of chlorine gas-induced lung injury.
Nanoparticles can turn off genes in bone marrow
Using specialized nanoparticles, researchers from Penn Engineering and MIT have developed a way to turn off specific genes in cells of bone marrow, which play an important role in producing blood cells.
Future collaborators and scientific pioneers at the Women in STEM symposium
Graduate students and faculty across Penn met to share their work and discuss solutions for issues faced by women in STEM.
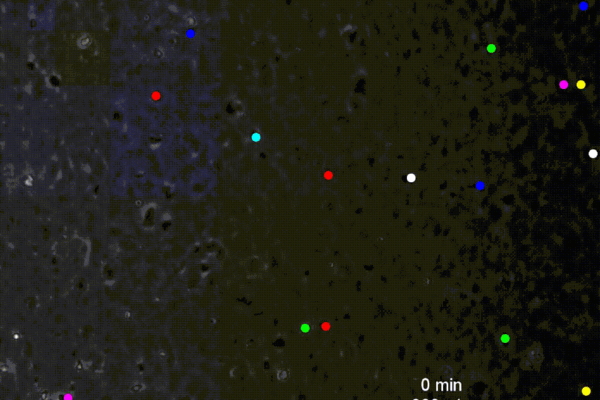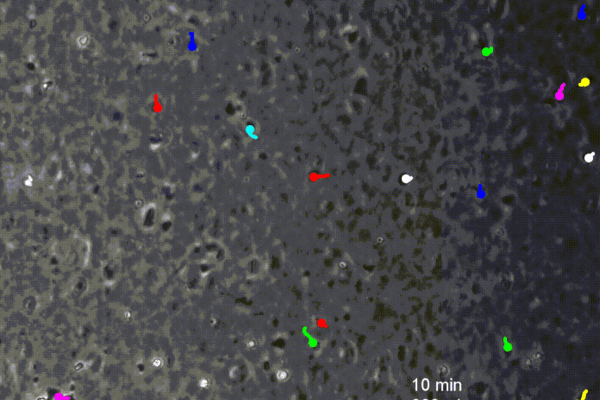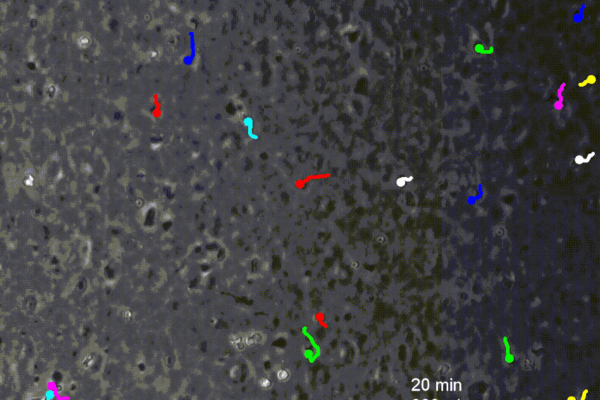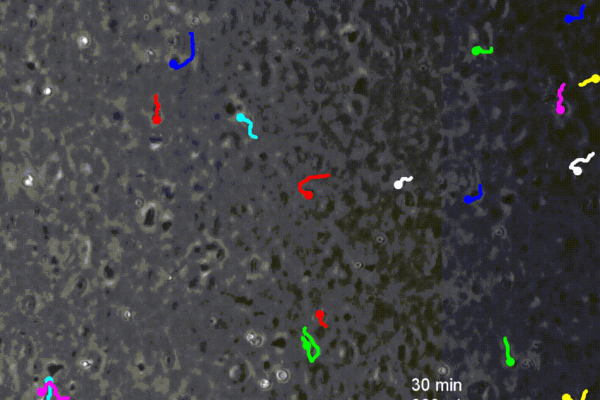
Engineers coax white blood cells to crawl upstream
Penn engineers find that by fighting the direction of the blood flow, white blood cells forge a faster route to battle infections.
Computer-generated antibiotics and biosensor Band-Aids
For Penn synthetic biologist César de la Fuente and his team, these concepts aren’t some far-off ideal. They’re projects already in progress, and they have huge real-world implications should they succeed.
Strella Biotechnology tackles food waste by ‘hacking the fruit’
President’s Innovation Prize awardees Katherine Sizov and Malika Shukurova are expanding their startup and confronting $1 trillion of food waste with their novel biosensing technology.
In the News
Can your personal medical devices be recycled?
A lab at the School of Engineering and Applied Science led the development of a COVID test made from bacterial cellulose, an organic compound.
FULL STORY →
Scientists think they’re on the verge of breaching the blood-brain barrier
Michael Mitchell of the School of Engineering and Applied Science and colleagues have constructed a model that could potentially allow drug transporters to bypass the blood-brain barrier.
FULL STORY →
How severed cockroach legs could help us ‘fully rebuild’ human bodies
David Meaney of the School of Engineering and Applied Science oversees an undergraduate bioengineering lab that uses cockroach legs to teach students to work with human prostheses.
FULL STORY →
Herniated discs could be repaired with biologic patch one day, researchers say
Preclinical research by Robert Mauck of the Perelman School of Medicine, Thomas Schaer of the School of Veterinary Medicine, and Ana Peredo, a Ph.D. graduate of the School of Engineering and Applied Science, reveals how a biologic patch activated by natural motion could become a key tool for repairing herniated discs in the back and relieving pain.
FULL STORY →
Thanks, Neanderthals: How our ancient relatives could help find new antibiotics
A study by César de la Fuente of the Perelman School of Medicine and colleagues used AI to recreate molecules from ancient humans that could be potential candidates for antimicrobial treatments.
FULL STORY →
Why CAR T cell therapy is the cancer killer the world needs now
Research from Michael Mitchell of the School of Engineering and Applied Science has developed a new method to stop cytokine release during CAR T cell therapy, preventing some of its more dangerous side effects.
FULL STORY →